Did you know that CSI can help you understand, in just one word, the health of your customer relationships? No, I don’t mean Crime Scene Investigator, although that might help in some cases. I am writing about the Customer Sentiment Index (CSI), a measure based on a single word that customers use to describe a company. The CSI is calculated using one-word responses from the following customer survey question: What one word best describes this company? Results show that the customer-generated words can be reliably scaled along a sentiment continuum and that these scores (CSI) are logically related to important customer experience metrics, like customer loyalty and satisfaction with the customer experience. The CSI is useful in helping businesses understand the health of their customer relationship. For the interested reader, details of the research on the CSI can be found in a series of blog posts (here, here and here). I recently presented this research at the Analytics Club MeetUp in Seattle. The slides appear below.
Measuring Customers’ Attitudes using Structured and Unstructured Data
 You can measure customers’ attitudes in two ways. One way to measure customer satisfaction, say, is to use an intentional approach where standard questions ask about their level of satisfaction. This approach requires a rating (structured data) from the customers. While there are different rating scales (1 to 5, 0 to 10, 1 to 7), the underlying premise of all of them is that the value of the rating scale is used as the measure of customer satisfaction. Lower ratings indicate lower satisfaction than higher ratings (e.g., 0 = Extremely Dissatisfied to 10 = Extremely Satisfied). Scores are customer-generated; customers convey their satisfaction through the ratings they choose to provide; customers who give higher ratings (say, a rating of 10) are more satisfied (have a more positive attitude) than customers who give lower ratings (say, a rating of 3).
You can measure customers’ attitudes in two ways. One way to measure customer satisfaction, say, is to use an intentional approach where standard questions ask about their level of satisfaction. This approach requires a rating (structured data) from the customers. While there are different rating scales (1 to 5, 0 to 10, 1 to 7), the underlying premise of all of them is that the value of the rating scale is used as the measure of customer satisfaction. Lower ratings indicate lower satisfaction than higher ratings (e.g., 0 = Extremely Dissatisfied to 10 = Extremely Satisfied). Scores are customer-generated; customers convey their satisfaction through the ratings they choose to provide; customers who give higher ratings (say, a rating of 10) are more satisfied (have a more positive attitude) than customers who give lower ratings (say, a rating of 3).
Another way to measure customer satisfaction is to apply sentiment analysis to unstructured text regarding what customers say about you (unstructured data). I refer to this approach as unintentional as the data are not generated to measure any particular construct. Formally, Wikipedia says “sentiment analysis (also known as opinion mining) refers to the use of natural language processing (NLP), text analysis and computational linguistics to identify and extract subjective information in source materials.” Unlike the use of structured questions and ratings, in sentiment analysis, scores of sentiment are generated by an algorithm; algorithms are used to assign a numerical value to what customers say. This numerical value (score) represents the customer’s attitude (from positive to negative) about your company.
In One Word
 I crafted a survey question that you can use in customer relationship surveys. This question asks the customer (respondent) to provide one word that best describes the company. As such, this measurement approach is designed to intentionally elicit descriptive words about the company. Customers are free to write anything for their response. I have used a couple of slightly different questions, but both appear to show similar results. The question is:
I crafted a survey question that you can use in customer relationship surveys. This question asks the customer (respondent) to provide one word that best describes the company. As such, this measurement approach is designed to intentionally elicit descriptive words about the company. Customers are free to write anything for their response. I have used a couple of slightly different questions, but both appear to show similar results. The question is:
What one word best describes this company?
Scoring the Customer Sentiment Index
To be useful in analysis, I needed to map each word along a sentiment continuum, essentially assigning each word a particular sentiment value. I developed a sentiment lexicon, a list of words that reflect an opinion on a negative-positive continuum, and this lexicon to this list of one-word responses to determine each word’s sentiment value. The sentiment lexicon is scaled from 0 (negative sentiment) to 10 (positive sentiment).
Correlates of the Customer Sentiment Index
I used the CSI in two independent studies, one using a B2B technology company and the other using a B2C wireless service provider company to determine if the CSI is related to other common CX metrics. Results from both studies showed that CSI scores were positively related to customer loyalty measures. Customers who have higher CSI scores also report higher levels of customer loyalty compared to customers with lower CSI scores. Additionally, CSI scores were more highly correlated (average r = .37, r = .46) with advocacy loyalty (i.e., overall satisfaction, recommend, buy same) than with purchasing (i.e., buy additional, expand use) and retention (i.e., renew) loyalty (average r = .18, r = .27).
Additionally, in both samples, CSI scores were positively related to each of the CX measures. Customers who have higher CSI scores also report higher levels of satisfaction with different CX touch points compared to customers with lower CSI scores.
Identifying At-Risk Customers Using the Customer Sentiment Index
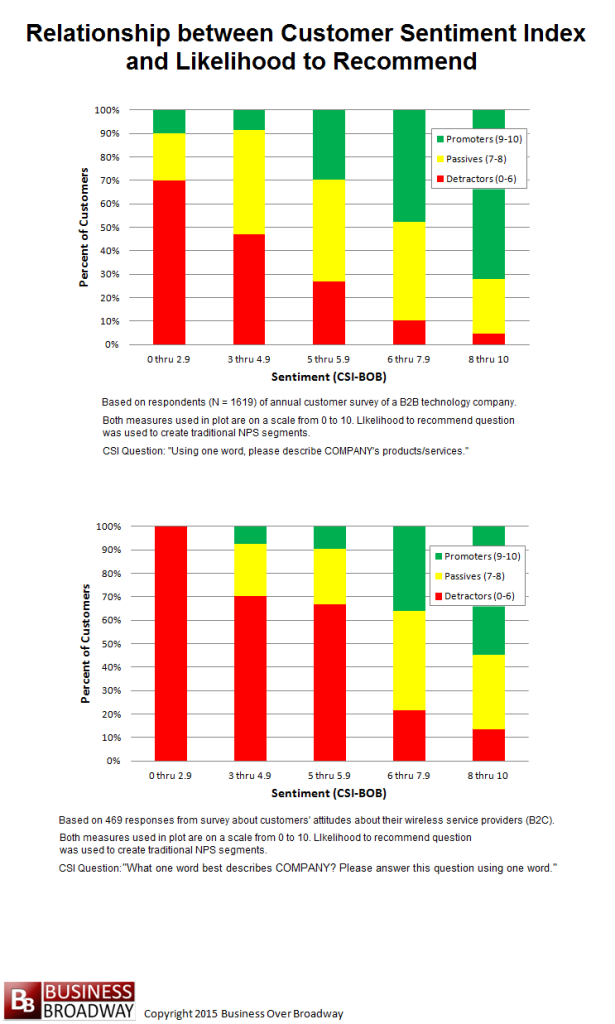
Figure 1. Relationship between the CSI and Likelihood to Recommend for both (B2B and B2C) study samples.
Customer surveys can be used to identify at-risk customers. “At-risk” is defined as those customers who will exhibit disloyal behaviors (e.g., switch) or those who will not exhibit loyalty behaviors (e.g., not recommend). I examined the relationship between CSI and the likelihood to recommend question (see Figure 1). The recommend question was grouped into segments made popular by the Net Promoter Score: Detractors, Passives and Promoters.
The relationship between the CSI and recommendation intentions was more linear for the B2B sample (top plot) compared to the B2C sample (bottom plot). For the B2B sample, the CSI cutoff point at which most respondents become Detractors is around 3.0. For the B2C sample, the comparable cutoff point for the CSI is around 6.0.
Summary and Implications
Asking customers to describe a company/brand using one word appears to hold value in helping businesses understand and manage the customer relationship. The Customer Sentiment Index (CSI) provides reliable, valid information about customers’ sentiment. The CSI measures customers’ general attitude about your company/brand.
The CSI was positively correlated with all customer loyalty and CX metrics. Customers with higher customer sentiment reported higher levels of customer loyalty and were more satisfied with their customer experience. The CSI was more closely associated with advocacy loyalty (e.g., overall satisfaction, likelihood to recommend) than with other types of loyalty and CX metrics, suggesting that the CSI measures customers’ general attitude toward the company.
As part of a customer experience management programs, businesses need to identify at-risk customers so they can address their concerns immediately. I illustrated how the CSI can be used to reliably identify at-risk customers (e.g., not likely to recommend). Setting the right cutoff point that optimizes the identification of loyal and disloyal customers varied across the B2B and B2C samples.
The process of using a single word as a measure of customer sentiment/satisfaction is useful for a variety of reasons:
- The CSI provides an good overall metric regarding the quality of the customer relationship. The CSI can augment current annual customer metrics. Rather than waiting an entire year to survey customers using traditional customer relationship surveys, businesses can easily employ the CSI to gauge customers’ attitude throughout the year.
- Customer experience professionals needs to optimize how they capture customer feedback in this mobile age. Soliciting customer feedback over mobile devices needs to be quick and easy for the customers. The CSI method is simple and easy for customers.
- Compared to traditional survey questions that require satisfaction ratings from the customers, the CSI method provides richer information about your customers. In addition to extracting sentiment from the words, the specific words themselves may provide some additional insight. For example, businesses can study specific words to understand the sentiment behind their usage and improve their customer communications by using words that resonate with certain customer segments. Interestingly, the two subject matter experts thought that word, “Expensive,” held a negative sentiment. In reality, the customers who used the word, “Expensive,” to describe the company were satisfied with the company.
- You can build your own sentiment lexicon for your company by including the CSI question and a rating question of overall satisfaction. Building specific sentiment lexicons for your business could help improve the predictive power of the CSI. Additionally, a company/industry-specific sentiment lexicon can be used for other analytics requiring natural language processing (e.g., analyzing sentiment of emails or of contact center conversations). Having a better lexicon helps you make better predictions and decisions.
- The methodology proposed here can be used to measure the sentiment of other stakeholders. For example, I used this one-word method in an employee survey to assess employee sentiment and found that an employee sentiment index could be useful to managing employee relationships.
The CSI measures the extent to which customers hold positive sentiment toward you. I will continue exploring different uses of the CSI to show how companies can use this metric in their customer experience management programs.
Content of this article originally appeared on CustomerThink.
For the interested reader, details of the research on the CSI can be found in a series of blog posts:




 Beyond the Ultimate Question
Beyond the Ultimate Question Measuring Customer Satisfaction and Loyalty (3rd Ed.)
Measuring Customer Satisfaction and Loyalty (3rd Ed.)
[…] recently developed a method to measure customer sentiment, the Customer Sentiment Index. This method combines a structured and unstructured approach to measuring attitudes. I’ve […]
[…] recently developed a method to measure customer sentiment, the Customer Sentiment Index. This method combines a structured and unstructured approach to measuring attitudes. I’ve […]
[…] recently developed a method to measure customer sentiment, the Customer Sentiment Index. This method combines a structured and unstructured approach to measuring attitudes. I’ve […]
[…] attitudes about a company's product or brand. This method is unique because it combines both a structured and unstructured measurement approach. Companies can use an open-ended survey question that asks customers to provide a single word that […]
[…] recently developed a methodology that combines both a structured and unstructured measurement approach.The methodology is based on a single open-ended survey question in which respondents are asked to […]